物理化学,青年研究员,博士生导师 复旦大学化学系研究员,国家海外青年人才项目入选者。2010年本科毕业于复旦大学化学系,2014年在美国约翰霍普金斯大学获得博士学位,随后赴美国北卡罗莱纳大学教堂山分校化学系、美国能源部能源前沿研究中心:太阳能燃料中心从事博士后研究。长期从事于可见光吸收分子敏化半导体薄膜界面的电子转移动力学研究,并把快反应动力学机理研究成果用于指导分子光伏电池和分子光电催化水分解器件的组装和提高太阳能转化效率。截至2024年共发表论文五十余篇,包括化学或材料类旗舰期刊 Nat. Chem.; J. Am. Chem. Soc .;JACS Au .; ACS Catalysis 等。 学习工作经历:2006.9-2010.6 复旦大学化学系本科,获...
查看更多>祝贺赵子建同学的文章“Nature-Inspired Photocatalytic Azo Bond Cleavage with Red Light”在线发表于
Journal of the American Chemical Society(JACS),并被选为封面文章(Cover Paper)


工作简介:
哺乳动物细胞中光氧化还原催化的新兴领域能够对大量生物过程进行时空调节。然而,低能可见光驱动的稳定共价键的选择性断裂仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在此,我们报道了市售染料(缩写为NMB+)的红光激发会导致水溶液和缺氧细胞中稳定偶氮键的催化裂解,因此是一种光递送药物或功能分子的方法。详细的机理研究表明,偶氮键断裂是由以前未知的连续双光子过程触发的。第一个光子产生三重激发态 3NMB+*,其被电子供体还原猝灭以产生质子化的NMBH•+。NMBH•+发生歧化反应,生成初始NMB+和二电子还原的NMBH(即无色NMB,缩写为LNMB)。有趣的是,LNMB与所有四种偶氮底物形成电荷转移复合物,在红色区域具有强吸收带。第二个红色光子诱导电子从LNMB转移到偶氮基板,导致偶氮键断裂。本文报道的电荷转移复合物介导的双光子催化机制让人想起黄素依赖性天然光酶,其利用高能光子催化键断裂反应。红光驱动的光催化策略为生物正交偶氮键断裂提供了一种新的方法,用于药物或功能分子的光递送。
文章摘要:
The emerging field of photoredox catalysis in mammalian cells enables spatiotemporal regulation of a wealth of biological processes. However, the selective cleavage of stable covalent bonds driven by low-energy visible light remains a great challenge. Herein, we report that red light excitation of a commercially available dye, abbreviated NMB+ , leads to catalytic cleavage of stable azo bonds in both aqueous solutions and hypoxic cells and hence a means to photodeliver drugs or functional molecules. Detailed mechanistic studies reveal that azo bond cleavage is triggered by a previously unknown consecutive two-photon process. The first photon generates a triplet excited state, 3 NMB+ *, that is reductively quenched by an electron donor to generate a protonated NMBH•+ . The NMBH•+ undergoes a disproportionation reaction that yields the initial NMB+ and two-electron-reduced NMBH (i.e., leuco-NMB, abbreviated as LNMB). Interestingly, LNMB forms a charge transfer complex with all four azo substrates that possess an intense absorption band in the red region. A second red photon induces electron transfer from LNMB to the azo substrate, resulting in azo bond cleavage. The charge transfer complex mediated two-photon catalytic mechanism reported herein is reminiscent of the flavin-dependent natural photoenzyme that catalyzes bond cleavage reactions with high-energy photons. The red-light-driven photocatalytic strategy offers a new approach to bioorthogonal azo bond cleavage for photodelivery of drugs or functional molecules. Zhao,Z . et. al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023
封面描述:The convergence of two beams of red light functions akin to a knife and fork set, effectively piercing and splitting the nitrogen–nitrogen double bond of azo compounds upon interaction with a photocatalyst.
原文链接:
https://www.x-mol.com/news/875131
恭喜赵子建同学荣获中国化学会第33届学术年会优秀墙报奖
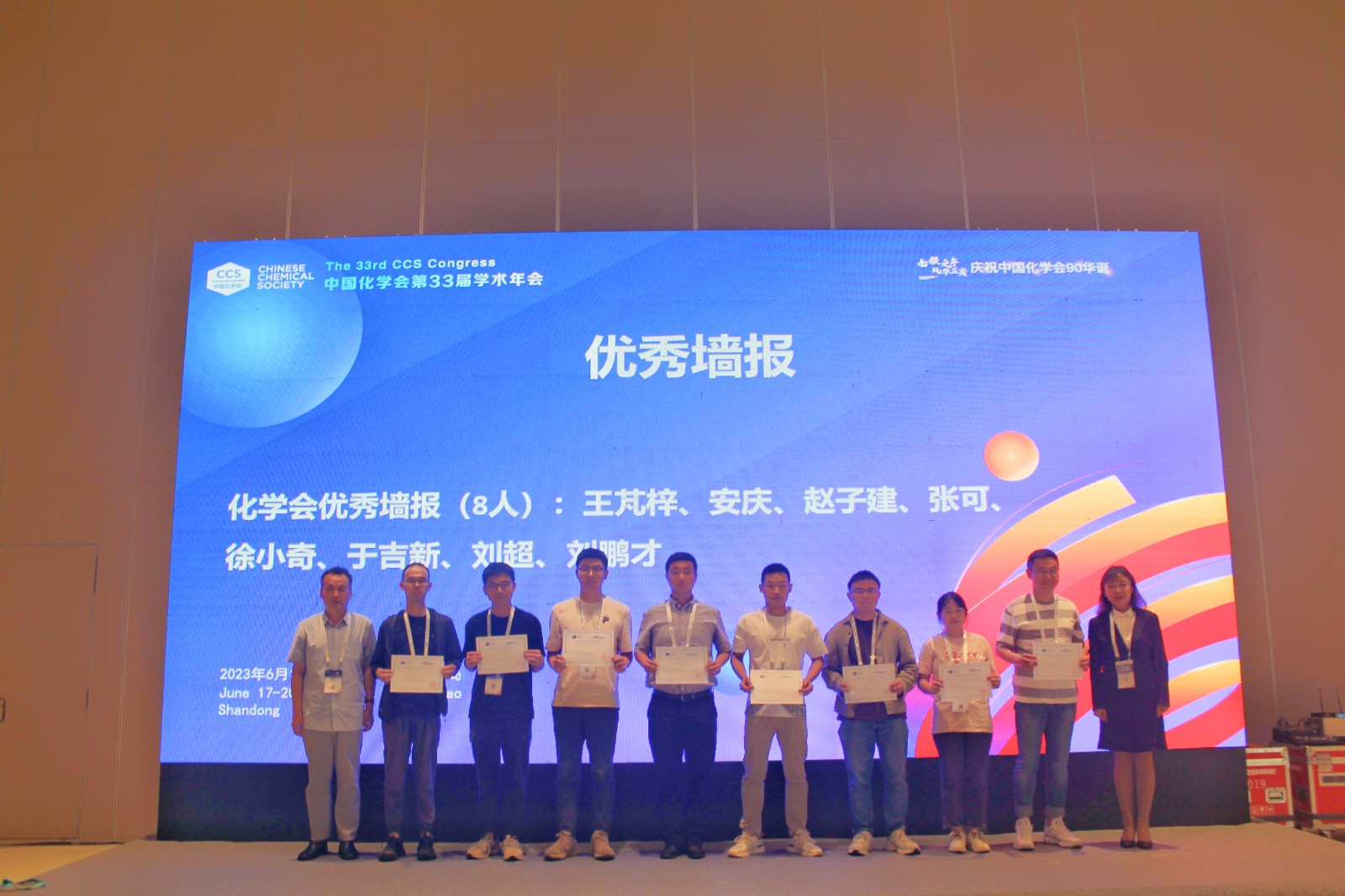


在2023年6月17至20日举行的中国化学会第33届学术年会上,赵子建同学参与了大会的优秀墙报评比
并脱颖而出,荣获优秀墙报奖,获奖墙报题目为“可见光激发创造微秒级长寿命超强还原剂”,
在此特向赵子建同学表示祝贺。
祝贺我组赵子建同学荣获2022年国家奖学金!
祝贺李鹏举同学的文章“Chloride Oxidation by One- or Two-Photon Excitation of N-Phenylphenothiazine”在线发表于
Journal of the American Chemical Society(JACS)
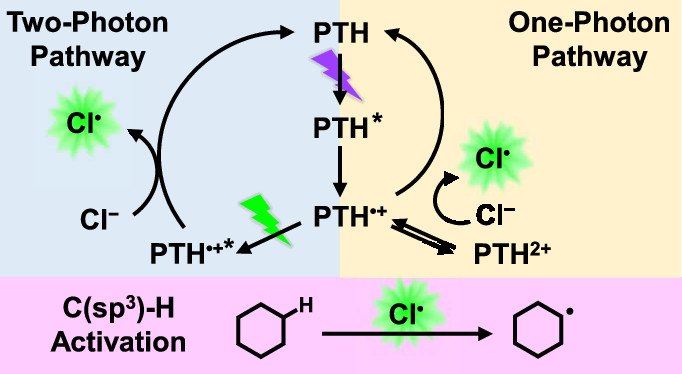
工作简介:
氯化物氧化在氯介导的 C-H 活化这一新兴领域具有巨大的实用性,但由于单电子还原电位E° (Cl •/– )非常正,因此它仍然是一个具有挑战性的过程。常见的过渡金属光氧化剂。本文介绍了两种光催化氯化物氧化途径,涉及N-苯基吩噻嗪 (PTH) 的单光子或连续双光子激发。单光子途径通过氧化猝灭产生 PTH • +,随后歧化产生 PTH 2+氧化氯化物;该途径也可通过 PTH 的电化学氧化获得。通过自由基阳离子激发态2 PTH • +*进行的双光子途径特别令人感兴趣,因为这种超级光氧化剂能够直接将氯化物氧化成氯原子。激光闪光光解表明,双激发态的光氧化通过静态猝灭机制在亚纳秒时间尺度上进行,离子对平衡常数为 0.36 M –1. PTH 光氧化还原化学在纳秒和更长的时间尺度上进行光谱量化,氯化物氧化化学通过与模型有机底物的反应性研究揭示。PTH 的单光子和双光子激发能够氯化有机化合物(如环己烷)的未活化 C(sp 3 )-H 键,从包含第二个激发波长观察到产率显着提高。这项研究为廉价且可商购的有机光氧化剂催化的氯化物氧化提供了新的机理见解。
文章摘要:
Chloride oxidation has tremendous utility in the burgeoning field of chlorine-mediated C–H activation, yet it remains a challenging process to initiate with light because of the exceedingly positive one-electron reduction potential, E° (Cl•/–), beyond most common transition-metal photooxidants. Herein, two photocatalytic chloride oxidation pathways that involve either one- or consecutive two-photon excitation of N-phenylphenothiazine (PTH) are presented. The one-photon pathway generates PTH•+ by oxidative quenching that subsequently disproportionates to yield PTH2+ that oxidizes chloride; this pathway is also accessed by the electrochemical oxidation of PTH. The two-photon pathway, which proceeded through the radical cation excited state, 2PTH•+*, was of particular interest as this super-photooxidant was capable of directly oxidizing chloride to chlorine atoms. Laser flash photolysis revealed that the photooxidation by the doublet excited state proceeded on a subnanosecond timescale through a static quenching mechanism with an ion-pairing equilibrium constant of 0.36 M–1. The PTH photoredox chemistry was quantified spectroscopically on nanosecond and longer time scales, and chloride oxidation chemistry was revealed by reactivity studies with model organic substrates. One- and two-photon excitation of PTH enabled chlorination of unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds of organic compounds such as cyclohexane with substantial yield enhancement observed from inclusion of the second excitation wavelength. This study provides new mechanistic insights into chloride oxidation catalyzed by an inexpensive and commercially available organic photooxidant. Li,P . et. al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022
原文链接:
祝贺牛富双同学的文章“Rapid Hole Extraction Based on Cascade Band Alignment Boosts Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation Efficiency”在线发表于ACS Catalysis
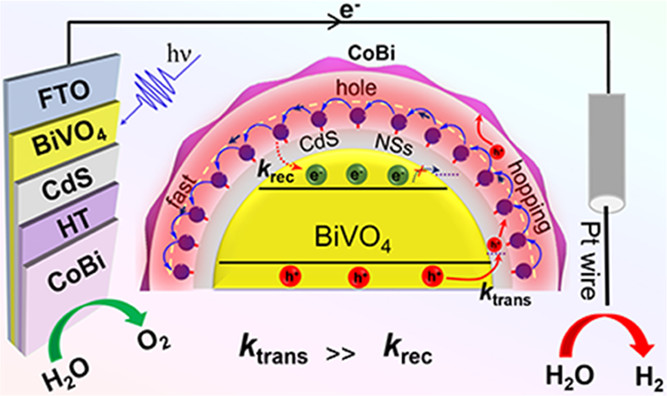
工作简介:
使用光电化学(PEC)分解水是一种将太阳能转化为化学能环保且可持续的方法。BiVO4(BVO)因其合适的带隙(2.4–2.5 eV)被认为是最有前途的光阳极材料之一。但是,BVO的空穴扩散长度很短,只有70 nm,因此电荷会在表面/电解质界面快速复合,这大大限制了BVO在PEC电池中的水氧化效率。界面电荷复合的光子能量损失是实现高效率的PEC水分解的关键挑战之一。
复旦大学化学系胡可课题组开发了一种基于级联能级排列提高空穴转移动力学并抑制电荷复合以促进PEC水分解的策略。设计原理如图1所示。在此,构建了基于BVO的光阳极,其中BVO、硫化镉纳米片(CdS NSs)、空穴传输分子(HTs)和析氧助催化剂(OECs)以级联能带排列顺序组装,实现了高效的光生空穴提取以及快速的OEC空穴累积。
文章摘要:
Photon energy loss to interfacial charge recombination is one of the key challenges to achieving high efficiencies for solar water splitting in photoelectrochemical cells (PECs). Herein, BiVO4-based photoanodes are constructed, where BiVO4, cadmium sulfide nanosheets (CdS NSs), hole transport molecules (HTs), and oxygen evolution cocatalysts (OECs) assemble sequentially in a cascade band alignment for efficient photogenerated hole extraction and accumulation to OECs. In the photoanode assemblies, CdS NSs act as energetic barriers to suppress surface recombination. Thiolate-functionalized aryl amine HTs that anchor to CdS NSs are interfacial-charge-transfer mediators that efficiently extract the photogenerated holes. The oxidized HT (HT+) hops isoenergetically among adjacent HTs and finally accumulates oxidative equivalents to OEC. Transient absorption spectroscopy along with intensity-modulated photocurrent spectroscopy proves that HTs and CdS NSs accelerate hole-transfer kinetics and suppress recombination of surface-accumulated holes and electrons. Among the three HTs, triphenylamine shows the best performance. The best-performing photoanode assembly exhibits increased photocurrent density from 0.87 to 5.2 mA/cm2. The molecular approach to hole extraction from BiVO4 photoanodes provides a promising avenue for efficient photogenerated charge separation and collection to optimize the performance of PEC for water splitting. Niu, F. et. al. ACS Catal. 2022
原文链接:
https://www.x-mol.com/news/781510
祝贺赵子建同学的文章“Visible Light Generation of a Microsecond Long-Lived Potent Reducing Agent”在线发表于
Journal of the American Chemical Society(JACS),并被选为正面封面文章(Front Cover Paper),审稿人之一将其
高度评价为“A very significant advance on a conceptual and on a methodological (synthetic) level”。

工作简介:
光敏剂分子的双重激发态结合了两个光子能量,可突破单个光子的能量限制,已被广泛研究证明其具有极强的氧化还原能力。这使得如脱卤反应、伯奇还原以及芳烃氧化等许多高需能反应在温和条件下(室温、可见光激发)成为可能。苝酰二亚胺型(PDI)光敏剂是最早发现也是研究最为广泛的具有连续可见光激发电子转移性质的一类光敏剂。然而前期的超快吸收光谱动力学研究表明,尽管2(PDI•–)*具有较强的还原能力,但其寿命只有约~160 ps。极短的光敏剂激发态寿命使其难以突破扩散限制将高能电子转移至底物,这极大地限制了利用连续光激发产生的超强还原剂的应用范围,一般只能应用于高底物浓度(mM~M)的有机合成中。
复旦大学化学系胡可(点击查看介绍)课题组与北卡罗来纳大学教堂山分校Gerald Meyer教授(点击查看介绍)合作,将PDI光敏剂通过水杨酸基团锚定在介孔纳米晶二氧化锆(ZrO2)(常被看作绝缘体)表面,可见光激发下,2(PDI•–)*的高能电子注入ZrO2导带中,形成的电荷分离态ZrO2(e–)|PDI使高能电子的寿命延长至~53 μs。相比PDI•–的激发态寿命,提升了近6个数量级。
文章简介:
Photoexcitation of molecular radicals can produce strong reducing agents; however, the limited lifetimes of the doublet excited states preclude many applications. Herein, we propose and demonstrate a general strategy to translate a highly energetic electron from a doublet excited state to a ZrO2 insulator, thereby increasing the lifetime by about 6 orders of magnitude while maintaining a reducing potential less than −2.4 V vs SCE. Specifically, red light excitation of a salicylic acid modified perylene diimide radical anion PDI•− anchored to a ZrO2 insulator yields a ZrO2(e−)|PDI charge separated state with an ∼10 μs lifetime in 23% yield. The ZrO2(e−)s were shown to drive CO2 → CO reduction with a Re catalyst present in micromolar concentrations. More broadly, this strategy provides new opportunities to reduce important reagents and catalysts at low concentrations through diffusional electron transfer. Zhao, Z. et. al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022
封面描述:
Visible light excitation of a perylenediimide radical anion results in electron injection into a ZrO2 insulator, yielding a potent reducing agent with a remarkable ~microsecond lifetime. The long-lived potent reducing agent provides new opportunities to reduce important reagents and catalysts present in low concentrations.
原文链接:
|
|
在2019年10月19日至21举行的能源化学与材料国际研讨会上,牛富双同学参与了大会的优秀墙报评比,
并在80份优秀的作品中脱颖而出,荣获优秀墙报奖。在此特向牛富双同学表示祝贺。
Copyright © 2019 复旦大学版权所有
沪ICP备:16018209-1
地址:上海市杨浦区邯郸路220号
邮编:200433